DC fast charging makes electric cars considerably more practical, allowing drivers to recharge a car’s battery to 80 percent of capacity in half an hour or less.
But quick charging was widely thought to come with a major drawback: While it lowers recharging times, research so far has indicated that fast charging shortens the lifespan of lithium-ion cells.
Now a new study published in the journal Nature Materials (via Green Car Congress) claims quick charging is less damaging than originally thought.
Fast charging itself was found to be less important for battery preservation than the distribution of current through the electrodes.
Led by researchers from Stanford University and the Stanford Institute for Material Sciences (SIMES), the study focused on the behavior of a lithium-iron phosphate cathode material.
Researchers built small coin-cell batteries and charged them with different amounts of current for various periods of time. The batteries were then disassembled and examined with an x-ray to see how they responded.
If a higher percentage of the nanoparticles in a cathode absorb and release ions during charging discharging, it will last longer. If only a smaller proportion are involved, the battery will gradually degrade.
After examining the test batteries, researchers found that only a small amount of nanoparticles were absorbing and releasing ions–whether fast charging or not.
However, they found that the distribution of ions became more uniform above a certain threshold.
The study’s authors say scientists may be able to take advantage of this effect to create longer-lasting batteries.
The next phase of this research will involve cycling batteries through hundreds–or perhaps thousands–of cycles to simulate real-world use.
Researchers also plan to x-ray batteries while they are charging to get a better idea of how the materials behave.
Meanwhile, electric-car owners are likely to continue using the growing number of DC fast-charging stations in the U.S.–but now they may be able to do so more confidently.

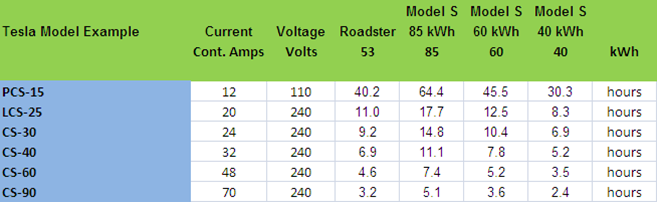
; ?>wp-content/themes/srptheme/images/Studion.png)